The Reality of Sex Trafficking in California
Human trafficking persists as a dark form of modern slavery in our Bay Area communities and across California, affecting both children and adults.
Understanding Human Trafficking
Human trafficking involves using force, fraud, or coercion to obtain labor or commercial sexual acts. For minors in commercial sex acts, the act itself constitutes trafficking under California law.
Accurate data remains challenging to obtain due to trafficking's hidden nature. While experts believe most cases go unreported, we present current California trends using available sources. This week, we focus on general trafficking trends and sex trafficking, with labor trafficking to be examined in next week's analysis.
_______________
California Trafficking Trends
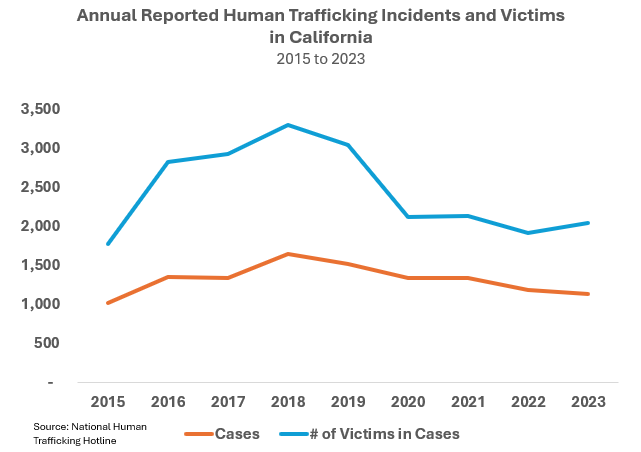
Data from the National Human Trafficking Hotline, a federally-supported 24/7 confidential resource, reveals significant patterns in California's reported cases:
Peak reporting occurred in 2018 with 1,646 cases involving 3,301 victims
Since this peak, there has been a 31% decline in reported cases
Identified victims have also decreased by 38%
_______________
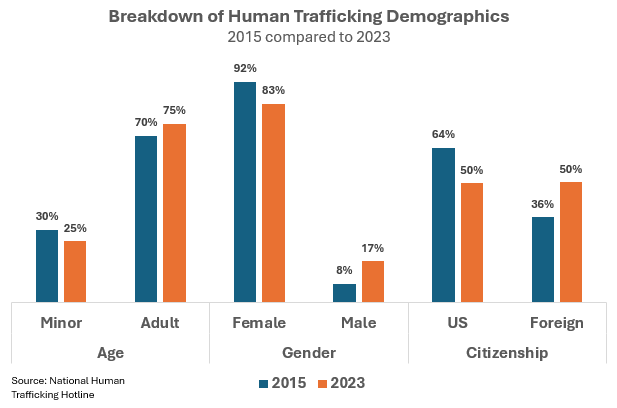
Trafficking victim profiles have shifted notably in recent years. As percentages of total reported cases:
Child victims fell from 30% to 25%
Male victims more than doubled, while females remain the majority
Foreign-born victims rose from 36% to 50%
_______________
Sex Trafficking
Sex trafficking accounts for 70% of reported trafficking cases, with data revealing distinct patterns in victim profiles and recruitment methods.
Victim demographics show a distribution across racial groups, with White victims at 27%, followed by Hispanic (23%), Asian (22%), and Black victims (19%).
These numbers help dispel misconceptions about who can become a victim.
_______________
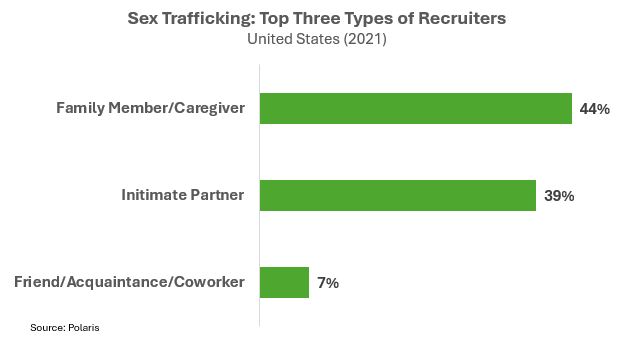
Most traffickers are known to their victims, with family members (44%) and intimate partners (30%) representing the majority of recruiters.
Traffickers often use online platforms to build intimate relationships and gradually coerce victims into commercial sex work, highlighting the importance of internet safety.
_______________
Understanding victim vulnerabilities is crucial for prevention. Key risk factors include recent migration/relocation, mental and physical health challenges, and unstable housing.
These circumstances can leave individuals particularly vulnerable to exploitation.
_______________
Effects of Sex Trafficking on Victims
Sex trafficking creates devastating physical, psychological, and social impacts that persist long after victims are freed. Sexual abuse and exploitation lead to severe physical trauma, reproductive health complications, and chronic medical conditions.
Key impacts include:
PTSD, depression, and anxiety from sexual trauma
Substance abuse issues, often introduced by traffickers for control
Sexual health complications and reproductive trauma
Economic exploitation through forced commercial sex acts
Severe isolation and disconnection from support systems
The psychological manipulation by sex traffickers – including threats, forced drug dependency, and emotional abuse – often destroys victims' sense of self-worth. Social stigma and shame create additional barriers to recovery.
_______________
Looking Forward
While significant challenges remain in combating trafficking, California has made meaningful progress through coordinated efforts and victim support programs. Supporting survivors requires ongoing community commitment to trauma-informed care and long-term recovery resources. By focusing on prevention strategies and comprehensive survivor care, we can continue to address this critical issue.
Next week, we'll examine labor trafficking in California, including detailed information about state and local response efforts, enforcement activities, and support programs.